What is #RDMA over converged Ethernet (#RoCE) and why we need it?
In the age of data, people have stricter requirements on the network. However, traditional TCP/IP Ethernet connections take up a lot of CPU resources and require additional data processing and copying which can no longer meet faster, efficient and scalable networks requirements. In this case, RoCE (RDMA over Converged Ethernet) goes into people's vision.
Why Need RDMA?
RDMA (Remote Direct Data Access) is developed to solve the delay of server-side data processing in network transmission. It can directly access the memory of one host or server from the memory of another host or server without using the CPU. It frees up the CPU to do what it’s supposed to do, such as running applications and processing large amounts of data. This both increases bandwidth and reduces latency, jitter, and CPU consumption.
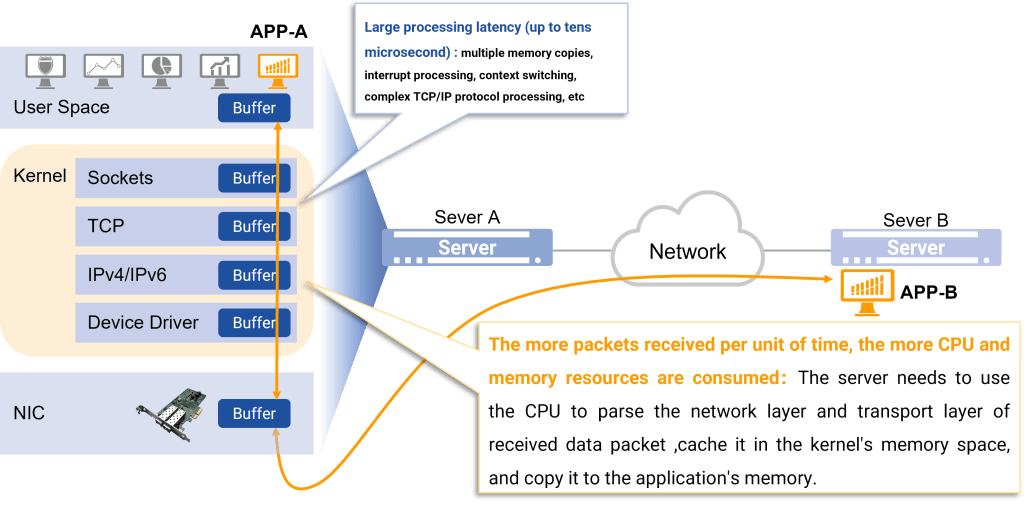
Therefore, RDMA can be simply understood as using related hardware and network technology, server A’s network card can directly read and write server B’s memory, resulting in high bandwidth, low latency.
As shown in the figure below, in RDMA mode, the application specifies the memory’s read and write address instead of participating data transfer process.

What is RoCE?
RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE) or InfiniBand over Ethernet is a network protocol that allows remote direct memory access (RDMA) over an Ethernet network. It does this by encapsulating an InfiniBand (IB) transport packet over Ethernet. In short, it can be seen as the application of RDMA technology in hyper-converged data centers, cloud, storage, and virtualization environments.
Type of RoCE
There are two RoCE versions, RoCE v1 and RoCE v2.
RoCE v1 is an RDMA protocol based on the Ethernet link layer (the switch needs to support PFC and other flow control technologies to ensure reliable transmission at the physical layer), allowing communication between any two hosts in the same Ethernet broadcast domain.
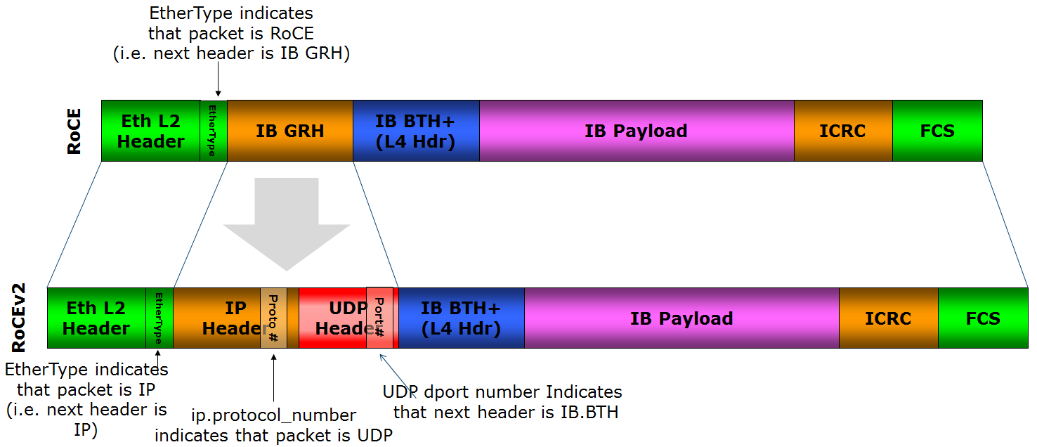
RoCE v2 overcomes the limitation of RoCE v1 binding to a single VLAN. RoCE v2 can be used across L2 and L3 networks by changing packet encapsulation, including IP and UDP headers.
How to Realize RoCE?
To implement RDMA for data centers, a network card driver and network adapter that supports RoCE can be installed. All Ethernet NICs require a RoCE network adapter card.RoCE is available in two ways: for network switches, you can choose to use switches that support PFC (Priority Flow Control) network operating system; for servers or hosts, you need to use a network card.
Comparison of RoCE, iWARP and InfiniBand
Currently, there are three types of RDMA networks: Infiniband, RoCE, and iWARP. Infiniband is a network designed for RDMA to ensure reliable transport from the hardware level, while RoCE and iWARP are Ethernet-based RDMA technologies that support the corresponding Verbs interface.
RDMA was first realized on the Infiniband transmission network with advanced technology but high price. Later, manufacturers transplanted RDMA to the traditional Ethernet network, reducing the use cost of RDMA and promoting the popularity of RDMA technology.
On Ethernet, there are iWARP and RoCE divided by stack integration. RoCE includes RoCEv1 and RoCEv2 (RoCEv2’s biggest improvement is IP routing). The following is the comparison of each RDMA network protocol stack.

- InfiniBand: supporting a new generation network protocol of RDMA. Since this is a new technology, NICs and switches that need to support it.
- RoCE: A network protocol that allows RDMA to be performed over Ethernet. Its lower network header is an Ethernet header, and its higher network header (including data) is an InfiniBand header. This enables the use of RDMA on standard Ethernet infrastructure (switches). Only NICs should be special and support RoCE.
- iWARP,a network protocol that allows RDMA over TCP. Features in IB and RoCE are not supported in iWARP. This enables the use of RDMA on standard Ethernet infrastructure (switches). Only NICs are special and support iWARP(if use CPU offload), otherwise all iWARP stacks can be implemented in software and most of the RDMA performance benefits are lost.
Advantages of ROCE
- Low CPU-take-up rate
- High efficiency
- Cost-effective
Asterfusion Marvell Teralynx based SONiC Switches Support ROCE
Asterfusion CX-N series switches preloaded with self-devlep SONiC NOS-AsterNOS can support RoCE v2/RDMA

Asterfusion High-Performance Cloud Network Empowers RDMA Applications
Asterfusion CEE:DCB &ECN ……

PFC creates an independent priority queue for RoCE flows

ETS provides the same level service for the same type RoCE flow and fully guarantees its bandwidth

CN provides end-to-end congestion notification for RoCE to solve congestion at the source

DCBX realizes automatic configuration of DCB parameters of RoCE network equipment

“ECN + Phantom Queueing” predict and avoid RoCE network congestion

VLAG upgrades RoCE reliability from link level to network level

Hardware-assisted intelligent traffic distribution algorithm reduces the faults on RoCE traffic

Intelligent Distribution of Several Flowlets of Elephant Flow in Asterfusion Cloud Network

Enable Distributed vL4LB to optimize RoCE traffic forwarding paths

Typical Application Scenarios for Asterfusion RoCE Solutions

评论
发表评论